By Todd Manley
Water management is a critical aspect of life in California, especially in regions like the Sacramento Valley where agriculture, fish and wildlife conservation, urban and rural communities, hydropower and recreation all rely heavily on water resources. In 2023, the Department of Water Resources revised the California Water Plan which sheds light on the intricate balance of water use throughout the state. Today, we delve deeper into the insights provided by this plan, focusing on how applied water is used to serve multiple benefits in the vital region of the Sacramento Valley.
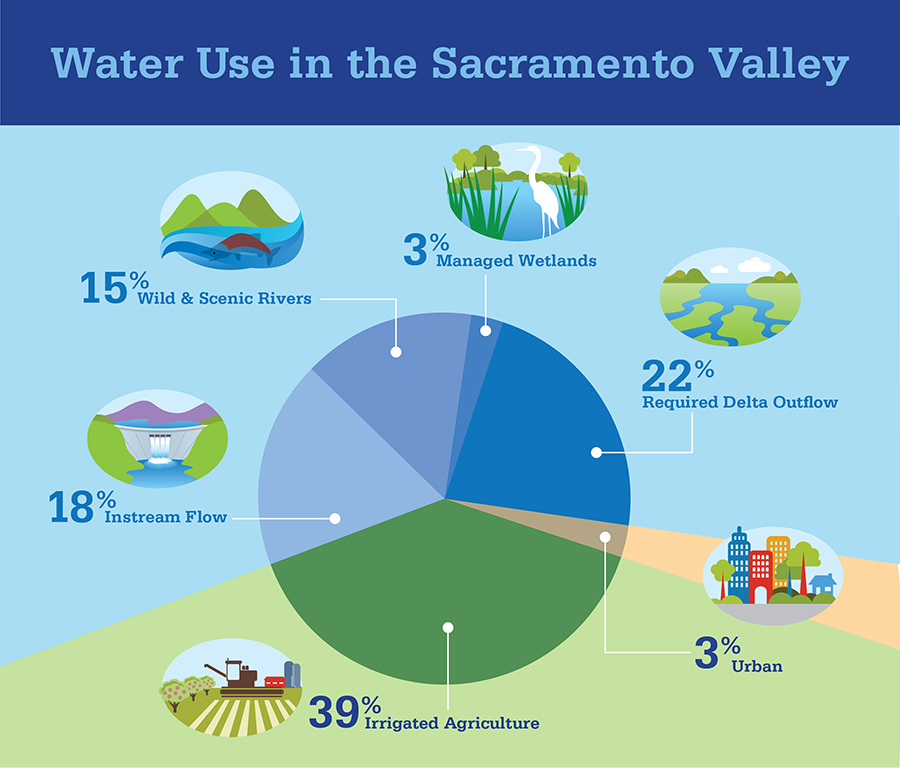
- Instream Flow: Dedicated to preserving the ecological integrity of rivers and streams, instream flow allocations ensure sufficient water levels for aquatic habitats, fish migration, and riparian ecosystems, promoting biodiversity and supporting recreational activities such as fishing and wildlife observation.
- Wild and Scenic River: Designated to protect the outstanding natural, cultural, and recreational values of select waterways, allocations for wild and scenic rivers prioritize conservation and sustainable management practices, safeguarding landscapes, habitat diversity, and recreational opportunities for future generations to enjoy.
- Managed Wetlands: Dedicated to preserving critical habitat for migratory birds, waterfowl, and other wildlife, allocations for managed wetlands support the maintenance and enhancement of wetland ecosystems, providing essential breeding, nesting, and foraging grounds while promoting biodiversity, flood control, and water quality improvement within the Sacramento Valley landscape.
- Required Delta Outflow: Essential for maintaining ecosystem health and water quality in the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta, the required delta outflow represents the volume of water necessary to meet regulatory mandates, control salinity levels, and preserve the delicate balance of biodiversity within the ecosystem.
- Urban Communities: Cities and towns within the Sacramento Valley rely on applied water for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes—from drinking water supply to sanitation and firefighting. Urban communities play a vital role in the regional water landscape.
- Irrigated Agriculture: The backbone of the region’s economy, agriculture accounts for a significant portion of applied water usage in the Sacramento Valley. Farms in the valley produce a wide array of crops, from rice and almonds to tomatoes and grapes, necessitating reliable water inputs.
State-Wide Water Use
While the Sacramento Valley exemplifies a unique blend of water uses tailored to its specific landscape and needs, water utilization patterns vary across the diverse regions of California. This pie chart shows how water is used during an average water year throughout the entire state.
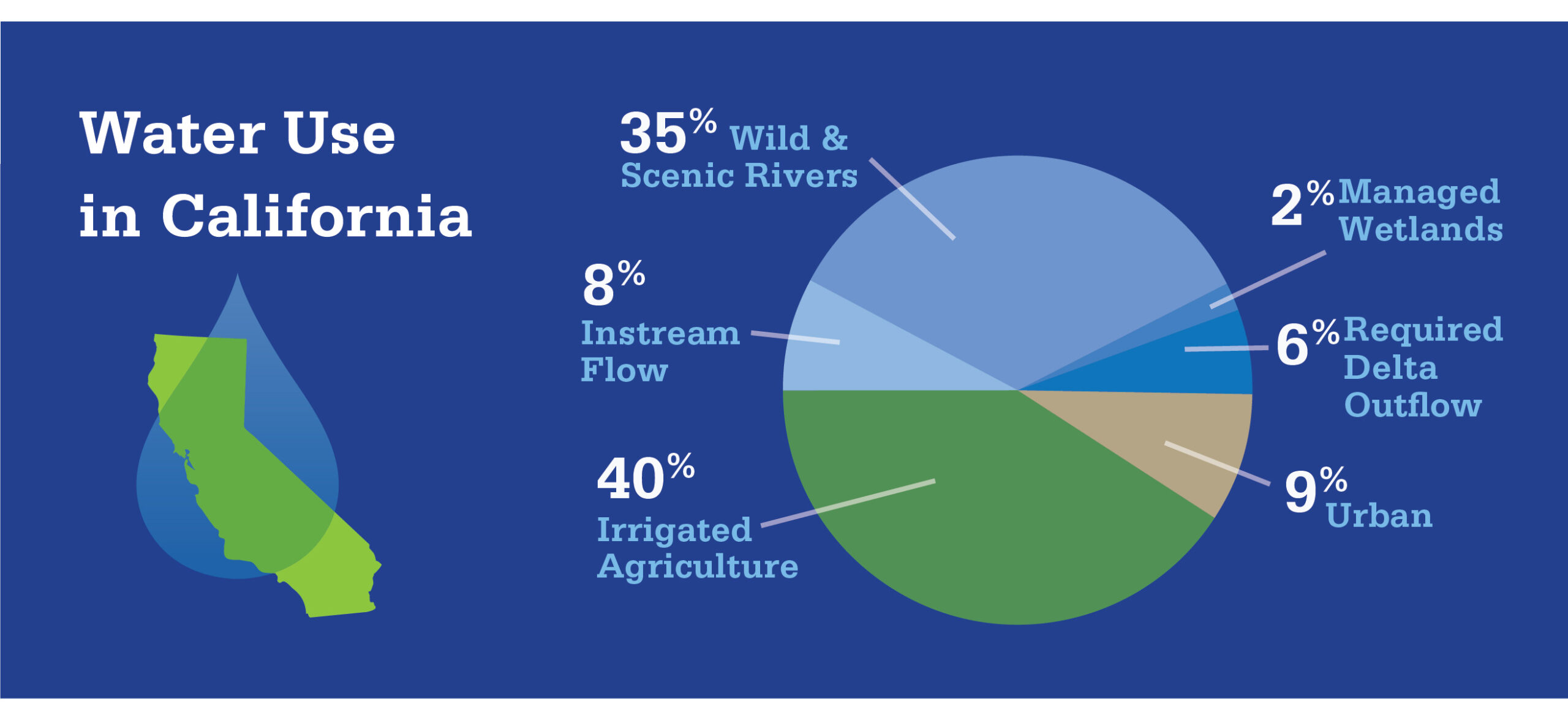
From agricultural heartlands in the Central Valley to bustling urban centers along the coast, and vast swaths of wildlife habitat located throughout the state, California’s water resources are allocated to support a wide range of beneficial uses. Understanding these nuances is essential for effective water management and sustainable resource stewardship statewide.
Source: California Water Plan at water.ca.gov/Programs/California-Water-Plan/Update-2023.